There are a lot to consider in determining which aspect of monopolistic competition gives consumers more choice, especially for a kind of competition that is commonly regarded as an imperfect competition.
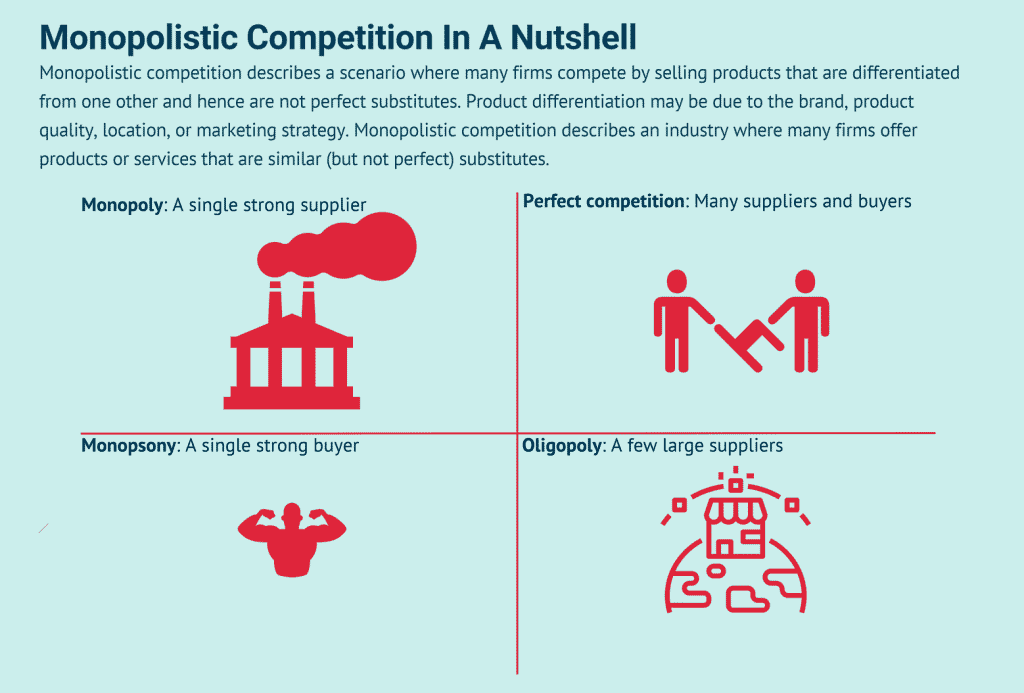
Competition and Monopoly are on the opposite ends of the board.
The monopolistic competition provides a market structure that lies between the competition spectrum of monopoly and competition.
It is a market structure where multiple companies in a particular industry produce highly similar products and are only differentiated by certain features that are most unique to themselves.
Each of the companies operate individually as separate from the other ones.
These companies usually make profit in the short run by virtue of the level of competition, and how often people go through the doors of its monopolistic competition.
It is unusual to see companies in an industry of monopolistic competition making large profits in the long run, such companies would have to be embodied with a quality so unique that makes them preferable to a good number of other companies in the industry.
Aspects of Monopolistic Competition
There are several qualities which upon their putting together, forms the concept of monopolistic competition.
Monopolistic competition, as earlier said, is a market structure whereby several companies in an industry deal in products whish are highly similar yet fairly distinctive.
The aspects of this business concept will now be shortly discussed thus:
- Multiple companies/sellers
- Product differentiation
- Barriers to entry and exit
- Standard and/or exceptional profits
#1: Multiple Companies/ Sellers
In monopolistic competition, there are many different large companies in the same industry.
They all deal in the same products or service which often results to an individual company being unable to make any huge difference in the marketing of its products, and thus, having the least influence over the decisions made by other competitors.
By reason of the number of companies in the industry, one company alone will be unable to make any significant economic gain in the long run.
One company alone will also be incapable of changing the price rate for their benefit.
Each individual company has a limited use, share and control of the market.
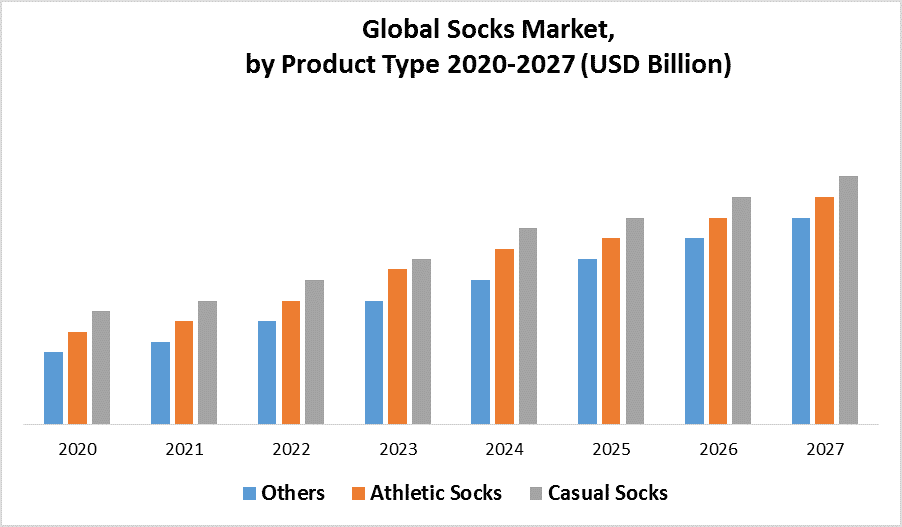
For instance, the industry of socks is very competitive – if one company decides to increase their price, consumers may simply move over to other brands, and if they choose to reduce it, they may either gain more consumers or lose more as the consumers may begin to undermine their product quality and move to other brands, therefore, leading to an economic loss.
#2: Product Differentiation
This is a strategy often adopted by firms where they imbibe certain exceptional qualities into their products which make them more attractive to buyers.
This strategy is often adapted by companies in an industry that is subject to monopolistic competition.
Competitors don’t depend solely on the market price for their incoming profit, but rather, on the quality and quantity of their products, as well as several other minute touches that make them more attractive to consumers.
Product differentiation could be seen in the quality, quantity, price, consumer relationship, service, reputation, packaging, advertisement, style or several other qualities as it relates companies in monopolistic competition.
#3: Barriers to Entry and Exit
In monopolistic competition, the barriers to entry and exit into the industries are usually very low. Often times, they barely exist or are non existent.
These business industries usually require easily affordable costs for starting up a business, and even if the cost is of an average amount, there isn’t that much likelihood of a sudden drop, except of course, it occurs from the producer/sellers part.
There’ also not a huge economic loss to be suffered upon exit of the business.
It should also be noted that it is not as easy as it may sound.
#4: Standard and/or Exceptional Profits
In monopolistic competition, profits usually come in at a normal level.
This is usually attributed to the fact that products here don’t necessarily have a specific season, and as such, they are always available for sale by virtue of the multiple options consumers usually have.
Basically, what could be gotten from one company, could also be gotten the other.
Must Read: What is the Best Bank for Small Business Checking Accounts?
This also implies that an “increase in price to increase profit” ratio may actually do more damage than good.
The profit that comes into the companies in these industries are usually at a normal rate. They don’t just get unexpectedly high in price as contrary to monopoly companies.
There are though, times when a company under monopolistic competition may get exceptional profits, but still, this can often be seen when a new brand or type just comes into the market, especially due to the fact that people often like to try out new items in the market.
In the fashion industry for example, once a company brings out a new fashion line, there is the tendency for people to indulge in it. People just generally want to wear what’s hot in the market.
At times like these, the profits that flow into the company are exceptional – they go beyond their standard rate of profits, even if it’s just for a period of time considering competition is always moving.
Which Aspect of Monopolistic Competition Gives Consumers More Choice?
When trying to know which aspect of monopolistic competition gives consumers more choice, we consider the following:
- Versatile decision making
- Price
- Easy access
- Consistent supply
#1: Versatile Decision Making
This is one major benefit which consumers of goods get to enjoy under monopolistic competition. This is by virtue of the fact that there are a large number of producers/sellers in the open market.
This gives consumers the freedom to choose from a variety of options and products.
Since the products are all similar, yet distinctive, this gives the buyer the freedom to choose according to their specifications.
There is also the possibility that a producer/seller may have exactly what they need.
Consumers are thus, always able to obtain a variety of products and services because they are all well-differentiated.
#2: Price
The price of goods and services in this kind of market are very favorable to consumers.
The price difference in commodities and services are not so high and are well easily affordable. If a particular brand is too high, the consumer may simply choose to buy from another brand or vendor.
#3: Easy Access
Goods and Services by firms in monopolistic competition are usually easily accessible.
They can often be found in every market and shop. For example, In Nigeria, bread is a pretty common commodity that is sold in literally every shop. This makes it easily affordable and accessible to all persons.
The bread industry can be seen as one that adopts monopolistic competition.
#4: Consistent Supply
Even if a consumer enjoys a particular brand or product, they will still be able to get a consistent supply for that product across different brands and companies in the industry.
By reason of the fact that the market is highly competitive, this goes to ensure that there is constant supply in the industry.
In reference to the bread example above, if one were to like bread rolls sold by a particular brand, and it’s one that easily affordable, sellers are more likely to sell it more so as to earn more profit for themselves.
This, in turn, leads to more supply, especially if this specific bread type has a better taste than others.
Products in monopolistic competition are usually supplied on a daily basis, and as such, consumers are sure to get it as often as they want and need them.






